How CBT Can Transform Your Mindset: Key Lessons from Mind Over Mood
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is one of the most widely used and evidence-based psychological approaches for managing thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. The book Mind Over Mood by Dennis Greenberger and Christine A. Padesky provides a practical, structured guide to applying CBT techniques to improve mental well-being. This article explores the core principles of CBT and how to apply them in daily life.The Thought-Feeling-Behaviour Cycle
At the heart of CBT is the understanding that our thoughts influence our emotions and behaviours.
✔ Thoughts (Cognitions): How we interpret events shapes how we feel.✔ Feelings (Emotions): Our emotional responses are linked to our thoughts, not just external events.
✔ Behaviours (Actions): Our actions often reinforce our thoughts and feelings.
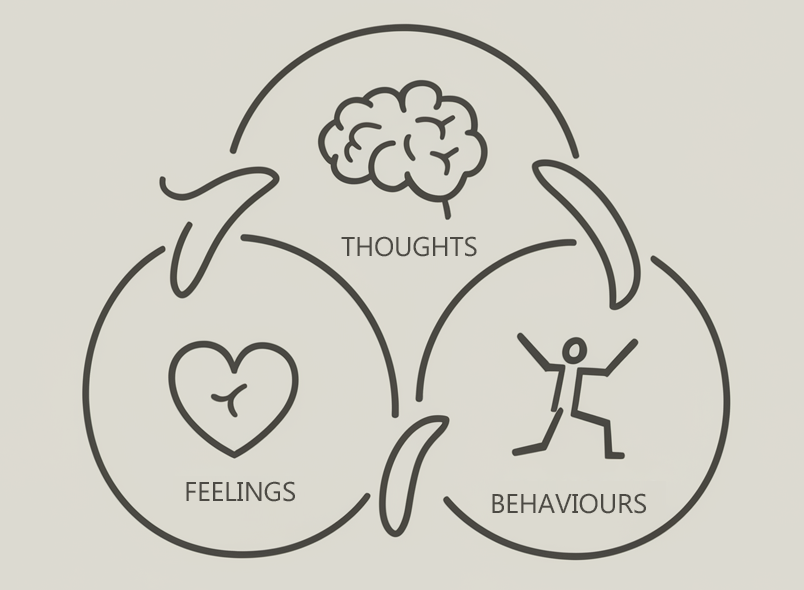
For example, if you believe, “I’m going to fail this presentation,” you might feel anxious and avoid preparing, which increases the likelihood of failure—reinforcing the original negative thought. CBT helps break this cycle by changing thought patterns and behaviours.
Identifying & Challenging Cognitive Distortions
Cognitive distortions are irrational or exaggerated thought patterns that contribute to emotional distress. Mind Over Mood outlines several common distortions:✔ All-or-Nothing Thinking: Viewing situations as black and white (e.g., “If I make one mistake, I’m a failure.”)
✔ Overgeneralisation: Assuming one bad experience means all future experiences will be the same.
✔ Catastrophising: Expecting the worst-case scenario (e.g., “If I don’t get this job, my career is over.”)
✔ Mind Reading: Believing you know what others think about you, often negatively.
✔ Personalisation: Taking responsibility for events beyond your control (e.g., “It’s my fault my friend is upset.”)
CBT helps identify these distortions and replace them with more balanced thoughts.
How Thought Records Work
A Thought Record is a structured CBT tool that helps examine and reframe negative thoughts. It involves:- Identifying the Situation: What triggered the negative thought?
- Recording Automatic Thoughts: What went through your mind?
- Noting Emotional Responses: What emotions did you feel and how intense were they?
- Evaluating the Evidence: What supports or contradicts this thought?
- Generating a Balanced Thought: What is a more realistic, constructive perspective?
Restructuring Core Beliefs
Core beliefs are deeply ingrained views about ourselves, others, and the world. They often develop in childhood and can be positive (e.g., “I am capable”) or negative (e.g., “I am not good enough”). Negative core beliefs fuel cognitive distortions and emotional distress.CBT helps identify and modify unhelpful core beliefs by:
✔ Recognising recurring negative patterns in thoughts.
✔ Testing beliefs through real-life experiences.
✔ Creating new, evidence-based beliefs (e.g., shifting “I am unworthy” to “I deserve kindness and respect”).
Practical Steps for Applying CBT in Daily Life
CBT techniques can be applied in everyday situations to improve emotional well-being:✔ Journaling: Regularly write down thoughts, emotions, and situations to identify patterns.
✔ Reality Testing: Ask yourself, “Is there real evidence for this thought?”
✔ Behavioural Experiments: Challenge avoidance behaviours by testing new approaches.
✔ Mindfulness & Relaxation: Reduce stress by grounding yourself in the present moment.
✔ Problem-Solving Strategies: Instead of ruminating, break problems into actionable steps.

